Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.32_1 - 32_13, 2023/12
Tensile deformation in situ neutron diffraction of an extruded AZ31 alloy was performed to validate conventional procedures and to develop new procedures for stress evaluation from lattice strains by diffraction measurements of HCP-structured magnesium alloys. Increases in the lattice strains with respect to the applied true stress after yielding largely vary among [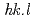 ] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [
] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [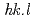 ] grains and evaluating them in many [
] grains and evaluating them in many [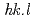 ] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple
] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple 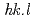 peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron source町屋 修太郎*; 長村 光造*; 菱沼 良光*; 谷口 博康*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Measuring the actual strain on the MgB filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB
filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
Li, S.; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; Deng, D.*
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/07
In this work, a framework was proposed on the comprehensive assessment of hardness and welding residual stress in Type 316 austenitic stainless steel welded joints. Firstly, an 8-pass butt-welded joint made of Type 316 stainless steel was fabricated. Finite element analysis of the welded joint was performed to investigate hardness and welding residual stress distributions. The grain growth model was developed for the hardness prediction. The Chaboche combined isotropic-kinematic strain hardening model and time-temperature dependent annealing model were adopted. The relationships between the Vickers hardness and the uniaxial plastic strain as well as grain size were collected from published literatures. The simulation results of the grain size and accumulated equivalent plastic strain were used for the hardness prediction of the welded joint. The predicted hardness was compared with the experimental data of hardness mapping. The distribution of welding residual stress on the outer surface of the welded pipe was measured by using the X-ray diffraction method and strain gauge method, respectively. The predicted welding residual stresses were compared with the measurements. The results obtained showed that the developed numerical approach can predict the hardness and welding residual stress of Type 316 stainless steel welded joints with satisfactory accuracy. The effects of structural constraint and heat input on the hardness and welding residual stress will be investigated as further works, as described in the proposed framework.
 X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; 冨永 亜希; 菖蒲 敬久; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)コバルトフリーのマルエージング鋼の強度特性を明らかにするために、高エネルギー放射光X線回折法を利用したその場引張試験を行った。マルテンサイト相とオーステナイト相からの回折プロファイルが得られ、それらの強度及び幅が負荷に伴い変化している様子が観察された。回折プロファイルを解析した結果、時効(as-aged)材では、低応力レベルにてマルテンサイトの含有量が緩やかに減少し、高応力レベルでは急激に減少した。一方、熱処理(as-solution)材では、応力の増加とともにオーステナイト相がマルテンサイト相に著しく転移変態している結果が得られた。これらのことがそれぞれの強度特性に起因していることを明らかにした。
山崎 泰広*; 篠宮 啓介*; 奥村 忠晴*; 鈴木 賢治*; 菖蒲 敬久; 中村 唯我*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
The suspension plasma spray (SPS) technique has attracted attention because of its various microstructures, which can be achieved by mixing submicron spray particles with a solvent to form a suspension. Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) with a columnar structure, which might achieve high strain tolerance, can be obtained using the SPS technique. In this study, the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC with different columnar structures was evaluated by hybrid measurement using high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis and laboratory low-energy X-rays. The effect of microstructure on the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC was discussed on the basis of the experimental results. In addition, the in-plane internal stress was decreased by decreasing the column diameter. The thin columnar microstructure of the SPS-TBC has superior strain tolerance. The internal stresses in the column of the SPS-TBC are periodic decrements caused by stress relaxation in porous layers.
西田 智*; 西野 創一郎*; 関根 雅彦*; 岡 勇希*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 鈴木 裕士; 森井 幸生*; 石井 慶信*
Materials Transactions, 62(5), p.667 - 674, 2021/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we used neutron diffraction to analyze in a non-destructive method the distribution of internal residual stress in a free-cutting steel bar processed by cold drawing and straightening. The residual stresses were successfully measured with excellent stress balance. The residual stresses generated by the cold-drawing process were reduced by subsequent straightening, and the distribution of residual stresses by finite element method (FEM) simulation was consistent with the measured values by neutron diffraction. As a result of the FEM analysis, it is assumed that the rod was subjected to strong tensile strains in the axial direction during the drawing process, and the residual stresses were generated when the rod was unloaded. Those residual stresses were presumably reduced by the redistribution of residual stresses in the subsequent straightening process.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_10, 2020/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:15.81(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) is essential for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. For RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), the assessment should be performed by considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. To assess the structural integrity of an RPV, a traditional method is usually employed by comparing fracture toughness of the RPV material with the stress intensity factor ( ) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,
) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,  of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on
of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on  calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for
calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for  calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
Wan, T.; 大林 寛生; 佐々 敏信
Nuclear Technology, 205(1-2), p.188 - 199, 2019/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To perform basic research and development to realize future accelerator-driven systems, a lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloy spallation target will be installed within the framework of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The target will be bombarded by high-power pulsed proton beams (250 kW, 400 MeV, 25 Hz, and 0.5 ms in pulse duration). The Beam Window (BW) of the spallation target is critical because it should survive under severe conditions that occur, i.e., high temperature, high irradiation, intense stress, and various kinds of damage. Therefore, the target vessel should be carefully designed to obtain an adequate safety margin. Our previous research indicates that there is a stagnant flow region in the LBE at the BW tip due to the symmetric configuration of the target, which causes high temperature and concentration of stress on the BW. On the basis of our previous work, three types of upgraded target head designs are studied in the current research to reduce/move the stagnant flow region from the BW tip and to increase the target safety margin. Thermal-hydraulic analyses and structural analyses for the target head designs are carried out numerically under a steady-state condition. Results illustrate that the designs can almost eliminate the stagnant flow region in the LBE. As a consequence, the concentration of thermal stress on the BW is released and greatly decreased. The safety margin of the target is improved through this study.
Lu, K.; 真野 晃宏; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 岩松 史則*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 140(3), p.031201_1 - 031201_11, 2018/06
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:45.47(Engineering, Mechanical)The stress intensity factor (SIF) solutions for subsurface flaws near the free surfaces of components, which are known to be important in engineering applications, have not been provided yet. Thus, in this paper, SIF solutions for subsurface flaws near the free surfaces in flat plates were numerically investigated based on finite element analyses. The flaws with aspect ratios a/l = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5, the normalized ratios a/d = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8, and d/t = 0.01 and 0.10 were taken into account, where a is the half flaw depth, l is the flaw length, d is the distance from the center of the subsurface flaw to the nearest free surface and t is the wall thickness. Fourth-order polynomial stress distribution in the thickness direction was considered. In addition, the developed SIF solutions were incorporated into a Japanese probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) code, and PFM analyses were performed for a Japanese reactor pressure vessel containing a subsurface flaw near the inner surface. The PFM analysis results indicate that the obtained SIF solutions are effective in engineering applications.
Wan, T.; 大林 寛生; 佐々 敏信
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 13 Pages, 2017/09
To realize the future Accelerator-driven systems (ADSs), an ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) will be constructed within the framework of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project to carry out basic R&Ds. A LBE spallation target will be installed in the TEF-T facility and be bombarded by high power pulsed proton beams (250 kW, 400 MeV, 25 Hz, 0.5 ms in pulse duration). The beam window (BW) of the spallation target is critical because it should survive under severe conditions, i.e., high temperature, high irradiation, intense stress and various occurred damage. Therefore, the target vessel should be carefully designed to obtain enough safety margin. Our previous research indicated that there are stagnant flow region in LBE at the BW tip due to the symmetric configuration of target, which causes high temperature and stress concentration on the BW. To reduce/move the stagnant flow region from BW tip and to increase the target safety margin, on the basis of our previous work, three types of upgraded target head designs were performed steadily in the present study. The thermal-hydraulic analyses and structural analyses for the target head designs have been carried out numerically under a steady-state condition. Results illustrated that the designs can almost eliminate the stagnant flow region in LBE. As a consequence, the thermal stress concentration on BW has been released and greatly decreased. The safety margin of target has been improved through this study.
青柳 和平; 名合 牧人*; 亀村 勝美*; 菅原 健太郎*
Proceedings of 9th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-9) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
Estimates of rock mass stress state and the mechanical characteristics of rock mass are important in the design of deep underground structures such as high-level radioactive waste disposal repositories. Stress measurements are conducted in boreholes to provide estimates of stress state. However, measurement results can vary highly as a result of rock mass heterogeneity, which causes difficulty in stress state evaluation. This study establishes a practical and effective method for estimating in situ stress based on the convergence measurement results obtained during gallery construction of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) project. The convergence was measured in various directions of the URL loop gallery to allow determination of the stress state over a large area. A back-analysis method was developed using the convergence measured during gallery excavation at 350 m depth. This method was applied to estimate the stress state corresponding to the rock mass behavior around the URL. The analysis results show good agreement with the in situ stress state reported in previous studies and confirm the applicability of the proposed method.
桑原 和道; 佐藤 稔紀; 真田 祐幸; 高山 裕介
JAEA-Research 2015-005, 378 Pages, 2015/07
本報告は、岩盤力学に関する調査研究のうち応力場の把握および岩盤の物理・力学特製の把握を目的として、瑞浪超深地層研究所の深度500mの研究坑道で実施した、深度500mを対象とした室内物理・力学試験、深度500mにおける円錐孔底ひずみ法による初期応力測定、深度500mにおけるDSCA法による初期応力測定、岩盤力学モデルの構築の成果を取りまとめたものである。
津坂 仁和*; 稲垣 大介*; 名合 牧人*; 井尻 裕二*
Proceedings of 8th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
This study describes the analysis performed on the West Access Shaft of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, which was expected to intersect a fault at the depth of approximately 320 m. Field observation, and measurement data were used to determine analysis conditions including magnitude and orientation of in-situ stress, boundary conditions, and rock mass properties. The fault was modeled as having a dip angle of 40 degrees and apparent thickness of 5 m (equivalent to the height of the excavated rock wall). The shaft sinking procedure was simulated using three-dimensional excavation analysis. The excavation involved installing concrete lining at every 2 m span. The analysis considered two cases of maximum in situ principal stress orientation: (1) perpendicular to and (2) parallel to the fault plane orientation. The results of the analysis indicate that the maximum excavation-induced stress, developed in a single-span lining concrete, was in the direction perpendicular to the maximum in situ principal stress orientation, unaffected by the fault plane orientation. The influence of the fault plane orientation on the excavation-induced stress state was found to be significant above and below the fault rather than in the fault. Another observation was that the excavation-induced stress magnitude appeared to be greater when the maximum in situ principal stress orientation was parallel to the fault plane orientation.
柴田 勝之*; 鬼沢 邦雄; 鈴木 雅秀; Li, Y.*
日本機械学会M&M2005材料力学カンファレンス講演論文集, p.299 - 300, 2005/11
改正電気事業法及び改正省令62号等が平成15年から施行され、構造機器の健全性に影響しない欠陥を残したまま運転継続が可能な維持基準が適用されている。運転継続にあたっては、欠陥の進展評価と健全性確認を行うことが必要である。応力腐食割れ等の進展には溶接残留応力が大きく影響するので残留応力の影響評価が重要である。現行規格では、影響関数により求めた応力拡大係数(K値)を用いて残留応力の影響を評価しているが、き裂進展とともに残留応力が解放されき裂先端には塑性域が生じるので、残留応力を荷重制御型の荷重として扱う影響関数法で求めたK値による進展解析が最適かどうかは疑問である。そこで、残留応力中をき裂が進展するときの残留応力の挙動を弾塑性解析し、残留応力の再分布の様子やき裂進展とK値との関係を求め、影響関数法によるK値と比較した。数種類の溶接残留応力中におけるき裂進展シミュレーションを行い残留応力の再分布及びK値の解析結果から、モデル長さの影響,端部拘束条件の影響,き裂先端部の塑性変形の影響を検討し、影響関数法によるK値を裂進展解析に適用した場合はき裂進展を過大評価することを明らかにした。
塙 悟史; 角田 淳弥; 柴田 大受; 石原 正博; 伊与久 達夫; 沢 和弘
Transactions of 18th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-18), p.600 - 605, 2005/08
炭素繊維強化炭素複合材料(C/C複合材)は高強度かつ優れた耐熱性を有することから高温ガス炉の炉内構造材として有望視されている。C/C複合材の原子力適用に際しては、黒鉛材料と同様に中性子照射による損傷がC/C複合材にも生じることが予想される。そこで、C/C複合材の熱・照射応力を評価するためにC/C複合材の高い異方性を考慮できる有限要素コードVIENUSを開発した。本報告では、炉心拘束機構への2次元C/C複合材の適用を想定し、C/C複合材の厚さや炉心拘束機構取付時のギャップをパラメータとした熱・照射応力解析を実施した。その結果、厚さとギャップの適切な設定によりC/C複合材は炉心拘束機構へ適用可能であること、また照射による寸法収縮に起因してC/C複合材に生じる周方向引張応力は増加するが、炉心拘束機構としてのC/C複合材の適用を考えた場合その増加は十分に小さいことが明らかとなった。
武田 信和; 大森 順次*; 中平 昌隆
JAERI-Tech 2004-068, 27 Pages, 2004/12
ITER真空容器はトリチウムや放射化ダスト等の放射性物質を閉じ込める安全機器である。本報告では、真空容器支持脚について、真空容器下部ポートから支持する独立支持構造を提案する。この独立支持方式は2つの利点を持つ。一つは、真空容器とトロイダル磁場コイルとの大きな温度差による熱荷重が軽減される点であり、もう一点は、トロイダル磁場コイルが真空容器と独立であることにより、安全機器として分類される必要がない点である。この支持脚の健全性を評価するため、真空容器の詳細モデルを用いて応力解析を実施した。その結果、真空容器とトロイダル磁場コイルとの相対変位は、設計クリアランスの100mmに対して15mmに押さえられた。また、支持脚を含む真空容器の応力はASMEで定められた許容値以下に押さえられた。これらの評価によって、提案する独立支持構造が真空容器支持脚として成立することが確認された。
武田 信和; 大森 順次*; 中平 昌隆; 柴沼 清
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1280 - 1286, 2004/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:23.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER真空容器はトリチウムや放射化ダスト等の放射性物質を閉じ込める安全機器である。現設計では、多層板バネによる真空容器支持脚はトロイダル磁場コイルに直接接続されているが、本論文では、真空容器下部ポートから支持する独立支持構造を代替案として提案する。この独立支持方式は現設計と比較して2つの利点を持つ。一つは、真空容器とトロイダル磁場コイルとの大きな温度差による熱荷重が軽減される点であり、もう一点は、トロイダル磁場コイルが真空容器と独立であることにより、安全機器として分類される必要がない点である。この支持脚の健全性を評価するため、真空容器の詳細モデルを用いて応力解析を実施した。その結果、真空容器とトロイダル磁場コイルとの相対変位は許容値100mmに対して15mmに押さえられた。また、支持脚を含む真空容器の応力はASMEで定められた許容値以下に押さえられた。これらの評価によって、提案する独立支持構造が代替案として成立することが確認された。
橘 幸男; 澤畑 洋明; 伊与久 達夫; 中澤 利雄
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 233(1-3), p.89 - 101, 2004/10
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:55.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)高温工学試験研究炉(HTTR)の反応度制御設備は、制御棒系と後備停止系から構成される。通常運転時、反応度は、16対の制御棒で構成される制御棒系により制御される。何らかの原因で制御棒を挿入できない場合は、後備停止系により、中性子吸収材である炭化ほう素ペレットを炉心内に落下し、原子炉を停止する。制御棒の構造材として、Alloy800Hが採用されているが、HTTRでは、スクラム時に制御棒温度が最高約900 Cに到達するため、新たに、設計基準及び材料強度基準を定めている。本論文は、制御棒の設計基準,材料強度基準及びこれらに基づく温度・応力解析結果並びに制御棒系と後備停止系に関する試験についてまとめたものである。(本論文は、HTTRに関するシリーズ投稿の一つである。)
Cに到達するため、新たに、設計基準及び材料強度基準を定めている。本論文は、制御棒の設計基準,材料強度基準及びこれらに基づく温度・応力解析結果並びに制御棒系と後備停止系に関する試験についてまとめたものである。(本論文は、HTTRに関するシリーズ投稿の一つである。)
西 宏
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part2), p.1567 - 1570, 2004/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:52.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)先に行ったステンレス鋼とアルミナ分散強化銅接合継手の低サイクル疲労試験の破壊点と疲労寿命について検討するため、弾塑性有限要素解析を用いて継手に引張変形及び繰返し変形を負荷したときの変形挙動を明らかにし、低サイクル疲労試験結果と比較した。その結果、次の結論を得た。(1)ステンレス鋼と分散強化銅の組合せは若干であるが応力特異性を有し、塑性域では弾性域に比べ特異性は減少するが、界面にひずみ集中が起こる。(2)解析より疲労試験片にはひずみ集中が起こり、ひずみ範囲が小さい時は界面近傍のアルミナ分散強化銅にひずみが集中し、ひずみ範囲が大きい場合は界面より離れたアルミナ分散強化銅側にひずみが集中する。(3)解析による接合継手の破壊点,疲労寿命は実験結果と一致し、接合継手の破壊点,疲労寿命は母材の疲労寿命から推定可能である。
高瀬 和之; 吉田 啓之; 小瀬 裕男*; 玉井 秀定
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.323 - 331, 2004/05
軽水炉の冷却材流路には燃料棒間のギャップ幅を一定に保つためにスペーサ等の突起がしばしば設置される。狭隘流路内のスペーサ周辺の熱流動に関する定量的な研究は、単相流では数多く見られるが、二相流ではほとんど見られない。そこで、狭隘流路に存在するスペーサ等の物体が二相流挙動に及ぼす影響を数値的に調べた。解析体系は3次元流路とスペーサを簡略模擬した矩形突起から成る。解析では、流路入口に液膜厚さとその流速及び蒸気流速を与え、時間方向に進展する液膜流挙動を非加熱等温流条件に対して定量的に検討した。本研究の成果は次のとおりである。(1)気液界面に作用するせん断応力によって界面不安定性が起こり、気相と液相の相対速度とあいまって波立ち発生へと現象が進行することを数値的に確認した。(2)突起後端から発生するはく離線に沿ってウエークが形成され、ここでは強い乱れによって液膜が排除されることがわかった。